Class 12
Unit 5 1
Object Oriented Programming
Procedural paradigm
- It is derived from structured programming.
- It is based on the concept of procedure call.
- Program code is divided into procedures, block of code.
- Procedures are known as routine, subroutines, methods or functions.
- It is also known as top-down language
- We can call any procedure at any point during a program execution
Object


- Objects can communicate without knowing the details of each
other's data or code. The only necessary thing is the type of message accepted
and the type of response returned by the objects.
- An Object is an identifiable entity with some characteristics and behaviour. An Object is an instance of a Class.
- When a class is defined, no memory is allocated but when it is instantiated (i.e. an object is created) memory is allocated
- Let us take an Example of a car object.
- A car object named “Maruti” can have data such as color; make, model, speed limit, etc. and functions like accelerate.
- For example: in real life, a car is an object. The car has attributes, such as weight and colour, and methods, such as drive and brake.

Advantages of procedural programming
- It is excellent for general-purpose programming.
- Easy to code/ source code is portable
- Code can be reused in different parts of program, without the need to copy it.
- Needs less memory
Structural programing
- It is also known as modular programming
- It emphasizes on separating a programs data from its functionality.
- Based on top-down methodology.
- Focus on dividing the program into sub parts, hence it simplifies problem solving.
- Eg: Algol, Pascal, Basic, C
Advantages
- Code is well organized
- Improved decision-making power.
- Easy to code and write program.
Object oriented programming
- Object-Oriented Programming is a methodology or paradigm to design a program using classes and objects.
- Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based upon objects (having both data and methods) that aims to incorporate the advantages of modularity and reusability.
- Objects, which are usually instances of classes, are used to interact with one another to design applications and computer programs.
- Benefits of object–oriented programming
• Modularity. Encapsulation
enables objects to be self-contained, making troubleshooting and collaborative
development easier.
• Reusability. Code
can be reused through inheritance, meaning a team does not have to write the
same code multiple times.
• Productivity. Programmers
can construct new programs quicker through the use of multiple libraries and
reusable code.
• Easily
upgradable and scalable. Programmers can implement system functionalities
independently.
• Interface
descriptions. Descriptions of external systems are simple, due to
message passing techniques that are used for objects communication.
• Security. Using
encapsulation and abstraction, complex code is hidden, software maintenance is
easier and internet
protocols are protected.
• Flexibility. Polymorphism
enables a single function to adapt to the class it is placed in. Different
objects can also pass through the same interface.
Features of Object oriented Programming
- Any entity that has state and behavior is known as an object.
- For example, a chair, pen, table, keyboard, bike, etc. It can be physical or logical.
- An Object can be defined as an
instance of a class. An object contains an address and takes up some space in
memory.
- Object means a real word entity such as pen, chair, table etc.
- It can be physical and logical.
- An object contains data and methods or functions that operate on that data.
- Objects take up space in memory.
- A variable, function, or data structure may all be considered an object
- Everything in C++ is associated with classes and objects, along with its attributes and methods.
- For example: in real life, a car is an object. The car has attributes, such as weight and colour, and methods, such as drive and brake.
- Attributes and methods are basically variables and functions that belongs to the class
- Object: Student
- Data: Roll no., Name:, and Grade
- Function: Study(), Sleep(), Playgame(), Calculate()
- Collection of objects is called class. It is a logical entity.
- A class is a blueprint for the object.
- Before we create an object, we first need to define the class.
- A class represents a collection of objects having same characteristic properties that exhibit common behavior.
- A class contains a skeleton of the object and does not take any space in the memory.
- Classes are data types based on which objects are created.
- Objects with similar properties and methods are grouped together to form a Class.
- Class is a template for objects, and an object is an instance of a class.
- When the individual objects are created, they inherit all the variables and functions from the class.
- Thus a Class represent a set of individual objects.
- Characteristics of an object are represented in a class as Properties.
- A class is a group of common behavior and functions
- For example a class fruit contains
- Apple, banana, Mango as a object.
- for example students, employee, fruits, car.
- Student class has: rollno, name, faculty, address.
- If mobile is a class then Samsung galaxy a32 is a object and its attributes are ram, memory, text, and calling
Encapsulations
- Encapsulation is the process of binding both attributes and methods together within a class.
- Binding (or wrapping) code and data together into a single unit are known as encapsulation. For example, a capsule, it is wrapped with different medicines.
- For example: capsule, it is wrapped with different medicines.
- Encapsulation is placing the data and the functions that work on that data in the same place.
- Real time examples, we encapsulate data and methods that operate on it by combining them into a single unit, the class.
- We can hide private information of a class from the outside world and only disclose functionality that is needed to interact with it this way.
- We say a class is properly enclosed when it prevents calling code from accessing its private data directly
- Through encapsulation, the internal details of a class can be hidden from outside.
- It permits the elements of the class to be accessed from outside only through the interface provided by the class.
- Encapsulation means containing all important information inside an object, and only exposing selected information to the outside world.
Examples
Realtime
Example 1:
- School bag is one of the most real examples of Encapsulation. School bag can keep our books, pens, etc.
Realtime
Example 2:
- When you log into your email accounts such as Gmail, Yahoo Mail there is a lot of internal processes taking place in the backend and you have no control over it.
- When you enter the password for logging, they are retrieved in an encrypted form and verified, and then you are given access to your account.
- You do not have control over it that how the password has been verified. Thus, it keeps our account safe from being misused.
Abstraction
- Hiding internal details and showing functionality is known as abstraction
- Data abstraction is the process of exposing to the outside world only the information that is absolutely necessary while concealing implementation or background information.
- Using abstraction in programming, we can hide unnecessary details from the user.
- Abstraction is the concept of object-oriented programming that “shows” only essential attributes and “hides” unnecessary information.
- The main purpose of abstraction is hiding the unnecessary details from the users.
- Abstraction is selecting data from a larger pool to show only relevant details of the object to the user.
- It helps in reducing programming complexity and efforts. It is one of the most important concepts of OOPs.
Real
life examples of abstraction
- For example: phone call, we don't know the internal processing.
- For example, when we ride a bike, we only know about how to ride bikes but can not know about how it work? And also we do not know the internal functionality of a bike.
- Another real life example of Abstraction is ATM Machine; All are performing operations on the ATM machine like cash withdrawal, money transfer, retrieve mini-statement…etc. but we can't know internal details about ATM.
Inheritance
- Inheritance in OOPs is a mechanism in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object.
- The Inheritance has many advantages, the most important of them being the reusability of code
- The reuse of existing classes saves time and effort.
- Inheritance is a process in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of its parent object automatically. In such way, you can reuse, extend or modify the attributes and behaviors which are defined in other class.
- Using inheritance object of one class can inherit or acquire the properties of the object of another class. Inheritance provides reusability of code.
- Inheritance is the process of forming a new class from an existing class
- It provides code reusability.
- Example: For instance, we are humans. We inherit certain properties from the class 'human' such as the ability to speak, breathe, eat, drink, etc.
- We can also take the example of cars. The class 'car' inherits its properties from the class 'Automobiles' which inherits some of its properties from another class 'Vehicles'.
Single inheritance
- When a class extends another one class only then we call it a single inheritance.
- The below flow diagram shows that class B extends only one class which is A.
- Here A is a parent class of B and B would be a child class of A.
Multilevel Inheritance
- In this inheritance, a derived class
is created from another derived class.
- In the given example, class c
inherits the properties and behavior of class B and class B inherits the
properties and behavior of class A.
- So, here A is the parent class of B
and class B is the parent class of C. So, here class C implicitly inherits the
properties and behavior of class A along with Class B i.e there is a multilevel
of inheritance.
Multiple inheritance
- In this inheritance, a derived class is created from more than one base class. This inheritance is not supported by .NET Languages like C#, F#, etc., and Java Language.
- In the given example, class c inherits the properties and behavior of class B and class A at the same level. So, here A and Class B both are the parent classes for Class C.
Hierarchical Inheritance
- In this inheritance, more than one derived class is created from a single base class and further child classes act as parent classes for more than one child class.
- In the given example, class A has two children class B and class C. Further, class B and class C both are having two children - class D and E; class F and G respectively
Hybrid inheritance
- This is a combination of more than one inheritance.
- Hence, it may be a combination of Multilevel and Multiple inheritance or Hierarchical and Multilevel inheritance Hierarchical and Multipath inheritance, or Hierarchical, Multilevel and Multiple inheritances.
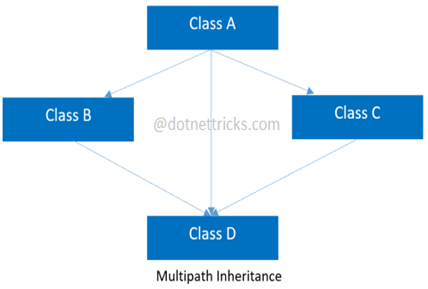
Multipath inheritance
- In this inheritance, a derived class is created from other derived classes and the same base class of other derived classes. This inheritance is not supported by .NET Languages like C#, F#, etc.
- In the given example, class D inherits the properties and behavior of class C and class B as well as Class A.
- Both class C and class B inherit the Class A. So, Class A is the parent for Class B and Class C as well as Class D. So, it's making it a Multipath inheritance.
Polymorphism
- Polymorphism means "many forms", and it occurs when we have many classes that are related to each other by inheritance.
- In simple words, we can define polymorphism as the ability of a message to be displayed in more than one form.
- It occurs when we have many classes that are related to each other by inheritance.
- Polymorphism allows us to perform a single action in different ways. In other words, polymorphism allows you to define one interface and have multiple implementations.
- The word “poly” means many and “morphs” means forms, So it means many forms.
- Examples of polymorphism
- A real-life example of polymorphism is a person who at the same time can have different characteristics. A man at the same time is a father, a husband, and an employee.
- So the same person exhibits different behavior in different situations. This is called polymorphism. Polymorphism is considered one of the important features of Object-Oriented Programming.
Advantages of Oops |
Disadvantages of Oops |
|
We can reuse the code multiple times using class |
Bigger program size |
|
Inherit the class to subclass for data redundancy |
It required a lot of effort to create |
|
It is easy to maintain and modify |
It is slower than other programs |
|
It maintains the security of data |
It is not suitable for some sorts of problems |
|
Low-cost development |
It takes time to get used to it. |
Application of Oops
•
Real-Time
System design: Real-time system inherits complexities and makes it
difficult to build them. OOP techniques make it easier to handle those
complexities.
•
Hypertext
and Hypermedia: Hypertext is similar to regular text as it can be stored,
searched, and edited easily. Hypermedia on the other hand is a superset of
hypertext. OOP also helps in laying the framework for hypertext and hypermedia.
•
AI
Expert System: These are computer application that is developed to solve
complex problems which are far beyond the human brain. OOP helps to develop
such an AI expert System
•
Office
automation System: These include formal as well as informal electronic
systems that primarily concerned with information sharing and communication to
and from people inside and outside the organization. OOP also help in making
office automation principle.
•
Neural
networking and parallel programming: It addresses the problem of
prediction and approximation of complex-time varying systems. OOP simplifies
the entire process by simplifying the approximation and prediction ability of
the network.
•
Stimulation
and modeling system: It is difficult to model complex systems due to
varying specifications of variables. Stimulating complex systems require
modeling and understanding interaction explicitly. OOP provides an appropriate
approach for simplifying these complex models.
•
Object-oriented
database: The databases try to maintain a direct correspondence between
the real world and database object in order to let the object retain it
identity and integrity.
•
Client-server
system: Object-oriented client-server system provides the IT infrastructure
creating object-oriented server internet(OCSI) applications.
•
CIM/CAD/CAM
systems: OOP can also be used in manufacturing and designing applications as it
allows people to reduce the efforts involved. For instance, it can be used
while designing blueprints and flowcharts. So it makes it possible to produce
these flowcharts and blueprint accurately.
Differences between Procedural Oriented Programming and object oriented programming
|
Procedural Oriented Programming |
Object-Oriented Programming |
|
In procedural programming, the program is divided
into small parts called functions. |
In object-oriented programming, the program is
divided into small parts called objects. |
|
Procedural programming follows a topdown
approach. |
Object-oriented programming follows a bottomup
approach. |
|
There is no access specifier in procedural
programming. |
Object-oriented programming has access specifiers
like private, public, protected, etc. |
|
Adding new data and functions is not easy. |
Adding new data and function is easy. |
|
Procedural programming does not have any proper way
of hiding data so it is less secure. |
Object-oriented programming provides data hiding so
it is more secure. |
|
In procedural programming, overloading is not
possible. |
Overloading is possible in object-oriented
programming. |
|
In procedural programming, there is no concept of
data hiding and inheritance. |
In object-oriented programming, the concept of data
hiding and inheritance is used. |
|
In procedural programming, the function is more
important than the data. |
In object-oriented programming, data is more
important than function. |
|
Procedural programming is based on the unreal
world. |
Object-oriented programming is based on the real
world. |
|
Procedural programming is used for designing
medium-sized programs. |
Object-oriented programming is used for designing
large and complex programs. |
|
Procedural programming uses the concept of procedure
abstraction. |
Object-oriented programming uses the concept of data
abstraction. |
|
Code reusability absent in procedural programming, |
Code reusability present in object-oriented
programming. |
|
Examples: C, FORTRAN,
Pascal, Basic, etc. |
Examples: C++, Java, Python, C#,
et |
Differences between Procedural Oriented Programming and object oriented programming
|
Structured Programming |
Object
Oriented Programming |
|
Structured Programming is designed which focuses on process/
logical structure and then data required for that process. |
Object Oriented Programming is designed which focuses
on data. |
|
Structured programming follows top-down approach.
|
Object oriented programming follows bottom-up
approach. |
|
Structured Programming is also known as Modular
Programming and a subset of procedural programming language. |
Object Oriented Programming supports inheritance,
encapsulation, abstraction, polymorphism, etc. |
|
In Structured Programming, Programs are divided into
small self contained functions. |
In Object Oriented Programming, Programs are divided
into small entities called objects. |
|
Structured Programming is less secure as there
is no way of data hiding. |
Object Oriented Programming is more secure as having
data hiding feature. |
|
Structured Programming can solve moderately
complex programs. |
Object Oriented Programming can solve any complex
programs. |
|
Structured Programming provides less reusability,more function dependency. |
Object Oriented Programming provides more reusability, less function dependency. |
|
Less abstraction and less flexibility. |
More abstraction and more flexibility. |